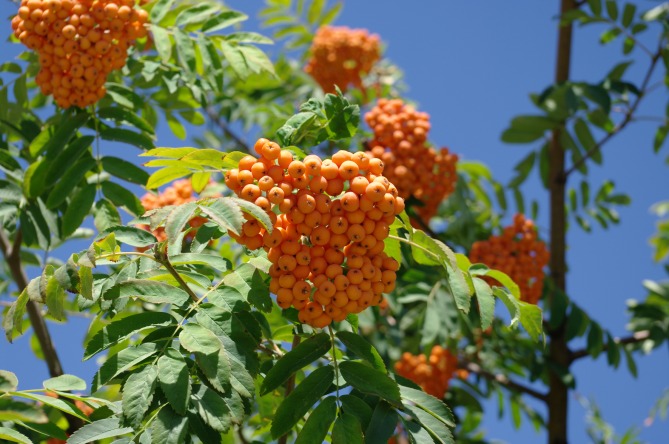
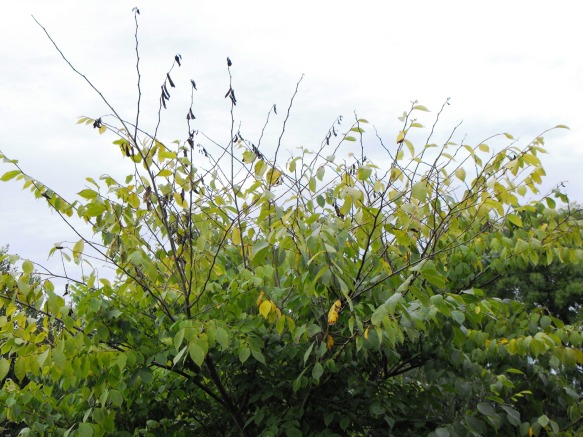
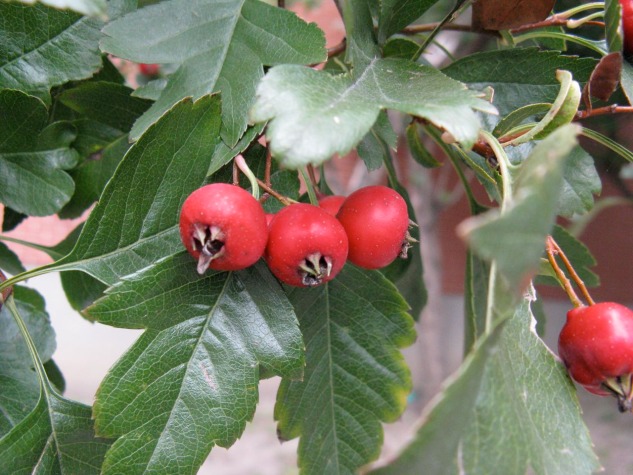
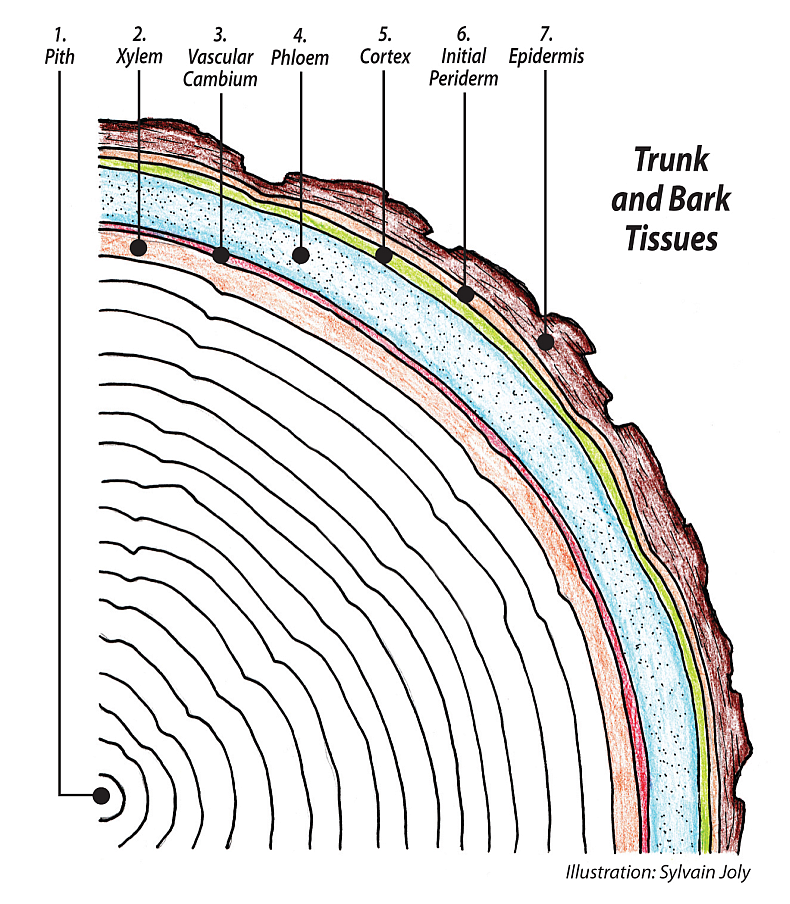
The genus Sorbus is our mountain ash, England's rowan tree. Always a favorite, there is just something about a mountain ash. Maybe it's the winter attraction with all those clusters of bright red fruit? The interesting compound pinnate leaves? Or the overall effect? But most people love mountain ash.
Native to North America, there are two mountain ashes that concern us, the showy and the American. Though difficult to differentiate, there are subtle changes in leaf shape, winter buds and flowers. The showy is named for its slightly latger flowers. By far, the American mountain ash is the most popular. With its robust form, chocolate brown colored bark, it is a striking tree.
Sorbus aucuparia, the European mountain ash, is also a good tree, with a lighter, sometimes almost yellow, bark and berries more orange. The European has two cultivars: the Russian, a more upright form and the fastigiata, a columnar form.
All three are good trees.
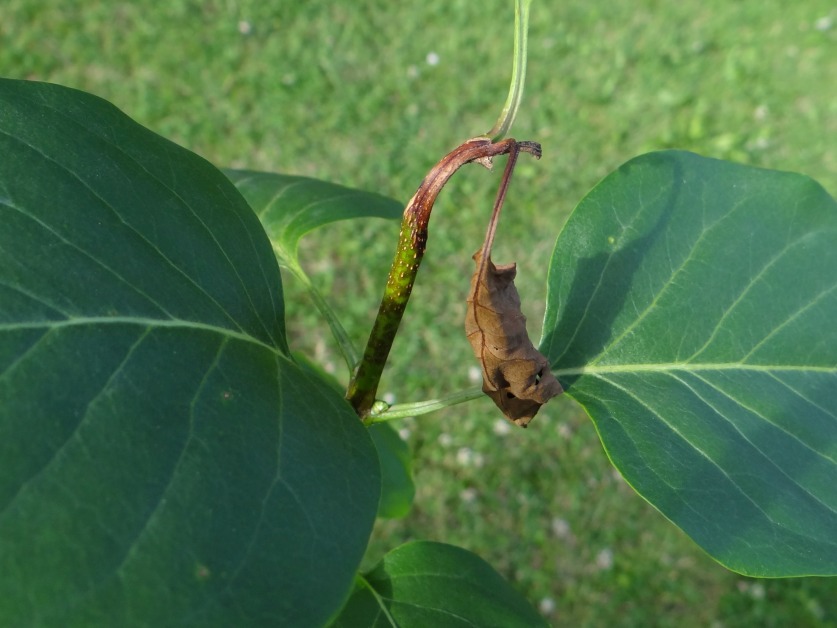
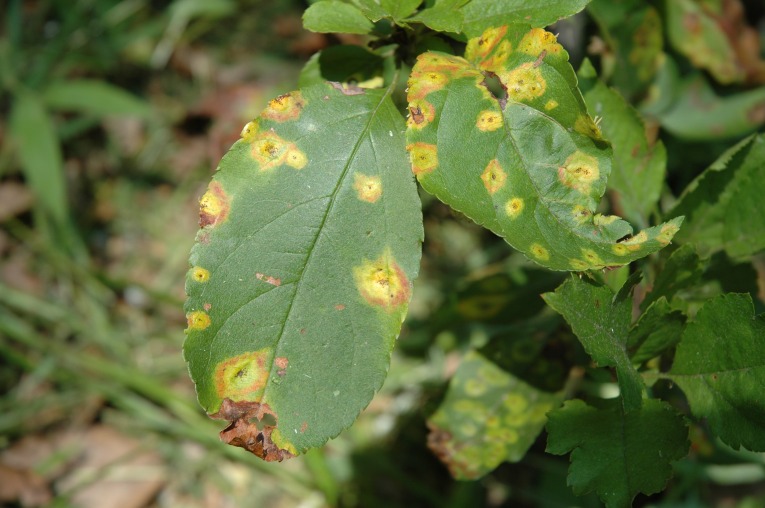
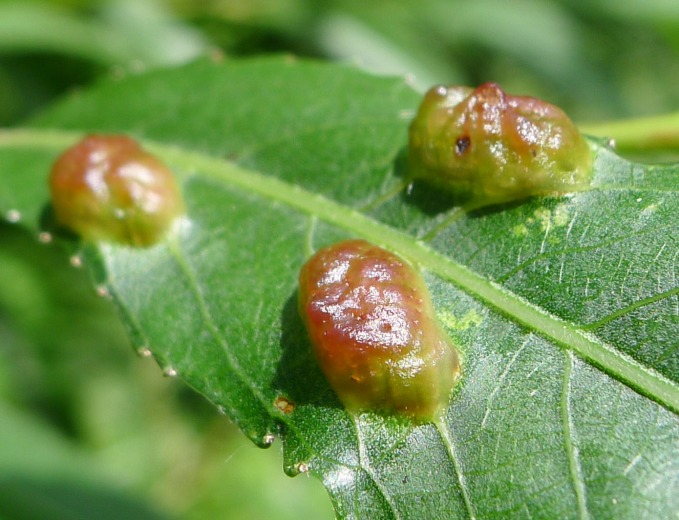
Mountain ash berries are a pome fruit, meaning that they are very much like little apples. They are highly susceptible to fire blight. Mountain ash have few insect problems, one that is conspicuous are the galls formed by the eriophyid mites. These microscopic insects live inside leaves and the tiny galls that form, little bumps really , are the leaves' reaction to the mites' activities. They are harmless; once inside the leaves there is no treatment. If this and many other insects caused any real harm to the tree it might be worth raising alarm. As is, this is just part of nature.
Tree Care Articles
Mountain Ash
- Details
- Written by Kevin R. Lee Kevin R. Lee
- Published: 03 November 2019 03 November 2019
Articles Index
- A Mind Set for Healthy Trees
- A New Tree Care Philosophy
- A Practical Working Model of Your Tree, Part One: Mostly Roots
- A Practical Working Model of Your Tree, Part Three: Leaves
- A Practical Working Model of Your Tree, Part Two: Trunk and Stem
- A weeping apple, some deer, and an arborist
- A Year in the Life of Your Tree - 1
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 2
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 3
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 4
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 5
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 6
- A Year In the Life of Your Tree - 7
- A Year in the Life of Your Tree - 8
- An arborist thinks on compartmentalization
- An Arborist's Education
- Ash Leaf-Cone Roller
- Ash Trees
- Aspens
- Birch
- Botany 1: The whole tree
- Botany 2: What do trees eat?
- Bud Scars
- Burning Bush
- Calgary Soils
- Calgary weather, snow pack, and the drought
- Calgary, from a tree's perspective
- Calgary's Most Dangerous, Dutch Elm Disease
- Calgary's most dangerous: Pseudomonas syringae
- Calgary’s most dangerous: Black knot
- Calgary’s Most Dangerous: Fire blight
- Calgary’s Most Dangerous: The Yellow-Headed Sawfly
- Caragana
- Caring For Your Trees This Winter
- Cell Walls
- Cherry Shrubs
- Cherry Trees
- Conifer Introduction
- Conifer Shrubs
- Conifers
- Cotoneaster
- Cranberries
- Currants
- Debunking Old Tree Myths
- Demystifying Tree Pruning
- Diagnosing Tree Problems
- Diplodia Gall of Poplar
- Dogwoods
- Dr. Alex Shigo
- Eating Apples and Other Hardy Prairie Fruit
- Elders
- Elms
- Epidermis
- Fall Needle Drop of Conifers
- Fertilizer
- Fertilizer 1
- Fertilizer 2: Trees
- First post Feb 23 2018
- Flowering Crabs
- Forsythia
- Fungal afflictions
- Growing Trees in Calgary
- Growing trees in Calgary, hands-on
- Haiku for spring
- Hardiness Zones
- Hawthorns
- Honeysuckles
- How to Have a Successful Tree
- Hydrangea
- In Defence, the Bronze Birch Borer (BBB)
- Introduction to Botany Talks
- Kate's Mayday
- Lack of connection
- Leaves
- Lilacs: French
- Lilacs: Pruning
- Linden
- List of Best Calgary Tree Choices - Evergreens
- Maintaining your pruning tools
- Maples
- Meristems: SAM and RAM
- Mid-Season Gratitude Post
- Mock Orange
- Mountain Ash
- Mugo Pines 1
- Mugo Pines 2
- Mugo Pines 3: Pruning
- My readers, my reasons
- Native Shrubs
- Needle Casts of Spruce
- Ninebark
- Oaks
- Ohio Buckeye
- Old Hacked Apple Trees -- Pruning a Tangle
- Organic Tree Work, Empowering Trees and People.
- Oyster Shell Scale
- Phloem
- Phomopsis Canker of Russian Olive
- Planting 1: Species selection
- Planting 2: Site selection
- Planting 3: Buying your tree
- Planting 4: Root crown identification
- Planting 5, Digging the hole, planting the tree
- Planting 6: Staking
- Planting 7: Watering
- Planting a Tree - Selection
- Planting a Tree - Setting, Staking and Watering
- Polemic and straight talk: the Swedish Columnar Aspen
- Poplars
- Proper Tree Pruning
- Pruning - More Reasons Why
- Pruning in Calgary with Nature in Mind
- Pruning Theory - Tools
- Pruning Theory - Why?
- Pruning tools you need
- Quotes
- Random thoughts from a Calgary Arborist and Tree Surgeon
- Reference books for Arboriculture
- Roots
- Russian Olive
- Septoria Canker on Poplar
- Shrub Introduction
- Shrub Pruning 1 - Theory
- Shrub Pruning 2 - Size Control
- Shrub Pruning 3 - Final
- Shrub Pruning for Size Control
- Shrub Pruning for Size Control 2
- Shrub Pruning Theory
- Slime Flux
- Soils - 1
- Soils - 2
- Spring?
- Stems
- Symptoms of a dry tree
- Symptoms of a sick tree
- The Mountain Ash
- The Three Cell Types
- Thinking of becoming an arborist?
- Toba Hawthorn: Pruning a tangle
- Tree Poem
- Tree Pruning Theory
- Tree Repair
- Tree Repair - 1
- Tree Repair - 2
- Tree Repair - 3
- Tree Repair - 4
- Trees and Their Interactions with Other Organisms
- Two Failures, Griffin Poplar, Manchurian Ash
- Vascular Cambium
- Walnuts
- Watering
- Watering a Birch
- Watering Calgary Trees
- Western Gall Rust of Pines
- What is Tree Whispering?
- When Should a Tree Be Removed?
- White Fly
- White Spruce
- Why is My Tree Dying?
- Willow Redgall sawfly
- Willows
- Wolf Willow
- Woolly Elm Aphid
- Xylem
- Yellow leaves: Chlorosis